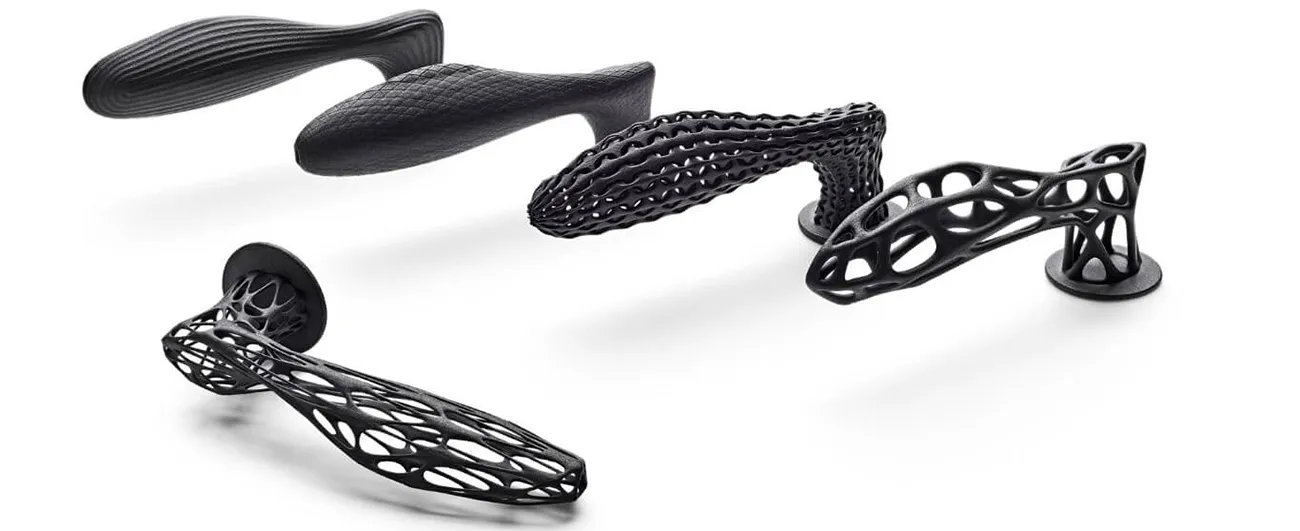

Every production process has specific requirements for product design, including additive manufacturing methods. Although many guidelines can be summarized under the term Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM), there are significant differences. This overview focuses on the Multi Jet Fusion process (Design for Multi Jet Fusion, DfMJF) and provides you with an initial insight. For detailed information on specific aspects of DfMJF, visit our dedicated pages.
1 Process

To better understand our component requirements and design, technical knowledge is helpful. Learn more about Multi Jet Fusion technology on our dedicated page, including:
- Our comprehensive and certified internal process chain.
- Material selection specific to Multi Jet Fusion.
- Overview of our finishing processes.
2 Dataset Requirements
A 3D model (CAD file) is essential for 3D printing, and for series productions, a detailed technical drawing is also recommended. In the second chapter, you will find more detailed information on the specific requirements for the 3D file, including formats and properties, as well as the necessary information for the technical drawing.
3 Basic Design Requirements

To ensure smooth production, Chapter 3 provides important information about key elements such as wall thicknesses, font sizes or detail resolution, minimum clearances, and minimum diameters for openings, holes, and channels.
4 Design Optimization & Functional Elements

Chapter 4 focuses on design optimizations and the integration of functional elements in 3D printing, based on the basic design requirements discussed in Chapter 3. It specifically addresses the integration of moving parts, hinges, fasteners, and threads in 3D models, as well as lightweight construction techniques.
5 Surface Optimization and Post-processing

In Chapter 5, you will find comprehensive guidelines for the treatment of surfaces, minimizing the stair-stepping effect, and avoiding warping. Additionally, it covers guidelines for post-processing techniques such as coloring or vapor smoothing. These guidelines are designed to optimize the aesthetics and quality of additive manufactured products.
6 Accuracy Optimization

Chapter 6 delves into the topic of accuracy optimization in the context of Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM), after addressing basic design requirements and strategies for optimizing functionality and surface quality in the previous chapters. It explores aspects such as tolerances and minimum dimensions for component elements and provides general recommendations for improving precision in additively manufactured parts. The goal of this chapter is to assist you in creating precise and high-quality 3D-printed objects.
7 Cost Optimization
Chapter 7 focuses on cost optimization. It demonstrates how targeted DfAM can reduce costs for 3D printing by addressing aspects such as volume reduction, build volume optimization, and the design of assemblies. The goal of this chapter is to help users maximize the benefits of additive manufacturing while minimizing costs.
- 1 Process, Materials, Post-processing, and more
- 2.1 CAD Data
- 2.1.1 Formats
- 2.1.2 Necessary properties of 3D models
- 2.1.3 Conversion & resolution of STL files
- 2.2 Technical Drawing for Additive Manufacturing
- 3.1 Wall thicknesses
- 3.2 Minimum & maximum object size
- 3.3 Font sizes
- 3.4 Holes & channels
- 3.5 Cavities
- 3.6 Joining objects
- 4.1 Moving parts
- 4.2 Hinges
- 4.3 Fasteners
- 4.4 Threads
- 4.5 Lightweight construction / Topology optimization
- 5.1 Top/bottom surfaces
- 5.2 Stair-stepping effect
- 5.3 Sinking/warping
- 5.4 Design considerations for post-processing in 3D printing
- 5.5 General recommendations
- 6.1 Tolerances
- 6.2 Minimum dimensions for component elements
- 6.3 Component orientation
- 6.4 General recommendations
- 7.1 Volume reduction
- 7.2 Build volume optimization
- 7.3 Assemblies
